Global temperature likely to be at least 1°C warmer in next 5 years says WMO
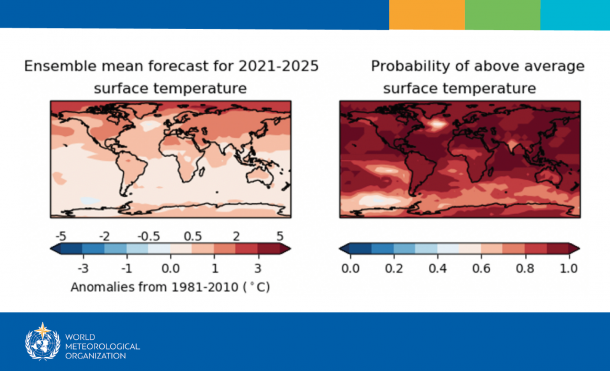
There is about a 40% chance of the annual average global temperature temporarily reaching 1.5°C above the pre-industrial level in at least one of the next five years – and these odds are increasing with time, according to a new climate update issued by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). There is a 90% likelihood of at least one year between 2021-2025 becoming the warmest on record, which would dislodge 2016 from the top ranking, according to the Global Annual to Decadal Climate Update, produced by the United Kingdom’s Met Office, the WMO lead centre for such predictions.
Over 2021-2025, high-latitude regions and the Sahel are likely to be wetter and there is an increased chance of more tropical cyclones in the Atlantic compared to the recent past (defined as the 1981-2010 average).
The Global Annual to Decadal Climate Update confirms that trend. In the coming five years, the annual mean global temperature is likely to be at least 1°C warmer – within the range 0.9°C – 1.8°C – than preindustrial levels. The chance of temporarily reaching 1.5°C has roughly doubled compared to last year’s predictions. This is mainly due to using an improved temperature dataset to estimate the baseline rather than sudden changes in climate indicators. It is very unlikely (10%) that the 5 year mean annual global temperature for the entire 2021-2025 period will be 1.5°C warmer than preindustrial levels, according to the climate update.
The Paris Agreement seeks to keep global temperature rise this century well below 2°C degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase even further to 1.5°C. National commitments to cut emissions, known as nationally determined contributions, currently fall far short of what is needed to achieve this target.
“These are more than just statistics,” said WMO Secretary-General Prof. Petteri Taalas. “Increasing temperatures mean more melting ice, higher sea levels, more heatwaves and other extreme weather, and greater impacts on food security, health, the environment and sustainable development,”
Information Source: Read Full Release ..–>

